What is PSD2?
The second EU Payment Services Directive (PSD2) builds on the first such Directive (PSD1) by providing for the further development of a better-integrated internal market for electronic payments across the EU.
PSD2 puts in place a comprehensive framework for payment services, with the objective of making payments within the EU more efficient and secure.
The Directive also aims to provide greater consumer protection by enhancing security measures for electronic payments. It seeks to open up payment markets to new entrants to encourage more competition.
***
Get weekly insights from The Intuition Finance Digest. Elevate your understanding of the finance world with expertly-crafted articles and podcasts sent straight to your inbox every week. Click here: https://www.intuition.com/finance-insights-the-intuition-finance-digest/
***
Background to PSD2
The fragmented nature of Europe’s payments markets has long been an irritation for those who would wish to see a more integrated European economy.
Added to that, the dominant role of major “foreign” card schemes such as Visa and Mastercard made new legislation for a more efficient and less costly European payments market an imperative for European authorities.
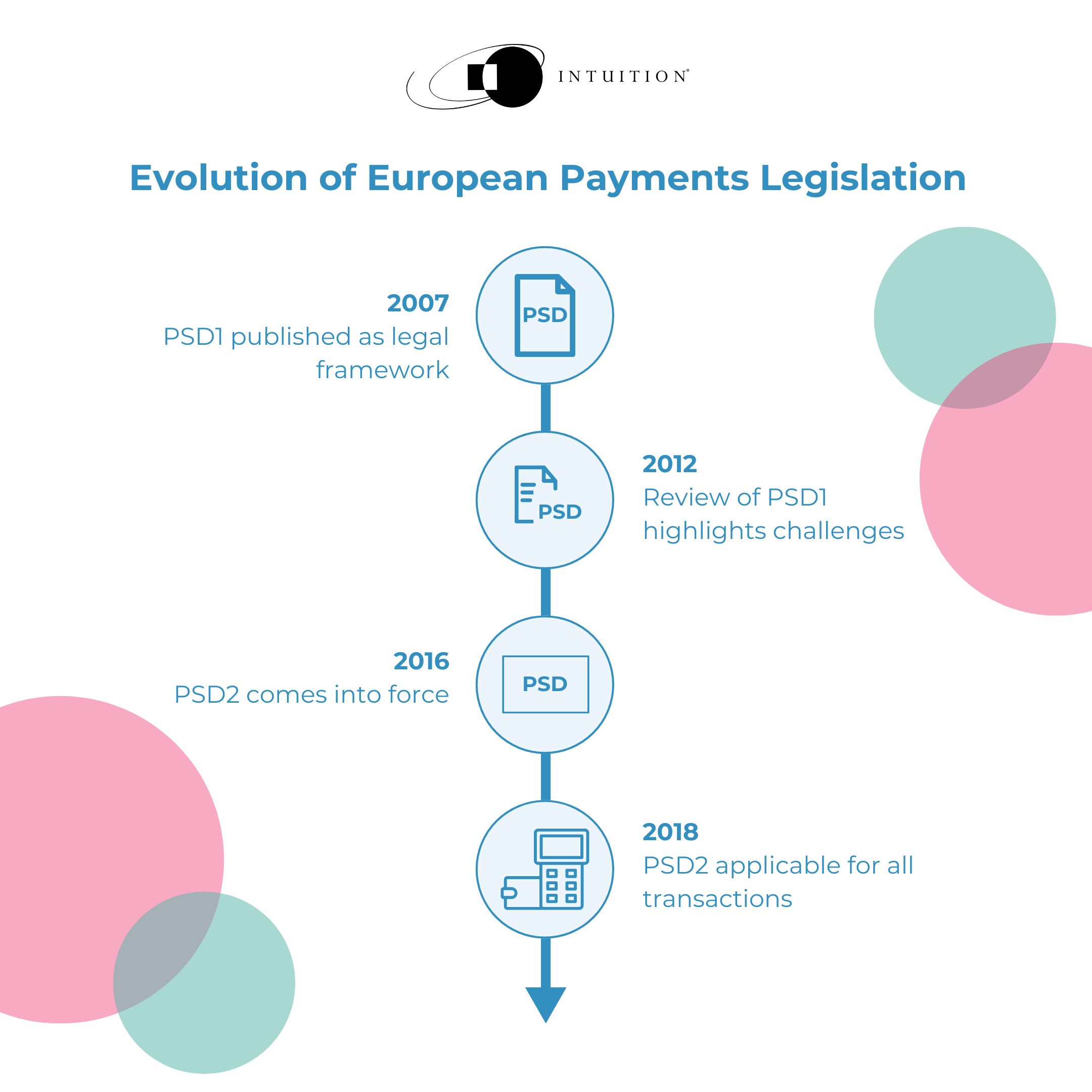
The first EU Payments Services Directive, PSD1 – published in 2007 – was intended to become the legal framework for all payments services within the EU and the European Economic Area.
PSD1 also provided a legal platform for the Single European Payments Area, or SEPA.
The overriding objectives of PSD1 were to:
- Promote competition by opening up the market for payments services across the continent
- Make cross-border payments as easy, efficient, and secure as making a payment within an EU state
Prior to PSD1, banks had traditionally dominated payments services in Europe. A major innovation of the Directive was the introduction of a new legal form of payment service provider, known as the “payment institution.”
Unlike banks, payment institutions are not permitted to take deposits from the public. They can only have access to customer funds when making payments on their behalf.
In addition to payment institutions, the Directive also defines the following categories of Payment Services Provider:
- Credit institutions
- E-money institutions
- Post office giro institutions
- The European Central Bank and national central banks
- Government ministries
PSD1 challenges
A review of PSD1 in 2012 found that while some of the Directive’s objectives had been achieved, there were still several challenges:
- An insufficient number of new providers were entering the market and the cost of payments to users was not falling significantly
- Payment institutions were still reliant on banks to help them offer their services
- PSD1 only covered payments within the EU
- The intervening years had seen the introduction of many innovative payments products not catered for by the Directive
These factors gave rise to the Second Payments Services Directive, PSD2, a revised and complete version of existing and new rules.
The introduction of PSD2
PSD2 came into force in January 2016 and was applicable from January 2018.
PSD2 set about eliminating the shortcomings of PSD1 by extending powers in three areas:
- It introduced so-called third-party providers that would be permitted to provide certain types of services related to payments
- It introduced strict security requirements for the initiation and processing of electronic payments and for the protection of customers’ financial data
- It extended the scope of PSD1 to transactions in all currencies and to payments where only one provider or party is located in the EU or EEA
PSD2 has proved to be transformational, not just in Europe, but potentially elsewhere.
Among other things, PSD2 gives third parties access to bank customer data and ushers in a new era of so-called “open banking.”
Intuition Know-How has a number of tutorials relevant to the content of this article, including:
- Payments – An Introduction
- Payments Methods
- Payments Rails & Participants
- Payments – Connectivity & Messaging
- Payments Cards
- Credit Cards
- Cards & Payments Programs
- Merchant Services
- PSD2 & Open Banking
Use Intuition Know-How to learn more about the world of payments.
Fill in the form below to browse the full tutorial offering.
Browse full tutorial offering



