Trends shaping the energy transition
The energy industry is currently undergoing a transformative phase, as it moves from traditional fossil fuels to renewable sources. Several trends are shaping the energy transition landscape, including the rapid growth of solar and wind energy, the increasing importance of hydrogen as a renewable energy source, and the global increase in electric vehicle (EV) adoption. This shift is primarily driven by the urgent need to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The energy transition is not just about merely replacing one source of power with another. It is about reshaping the entire energy ecosystem, including infrastructure, technology, policy, and market dynamics. The paradigm shift involves a multi-dimensional approach that requires active participation and collaboration from governments, businesses, and consumers alike.
The journey toward a sustainable energy future is complex and challenging, but it also offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation, growth, and resilience.
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the key trends that are driving the energy transition and their implications for the global energy landscape.
The rapid growth of solar and wind energy
One of the most significant trends shaping the energy transition is the rapid growth of solar and wind energy. These two renewable sources have emerged as the frontrunners in the green energy race, thanks to their abundant availability, falling costs, and technological advancements.
Solar energy, in particular, has seen dramatic growth over the past decade. The advent of photovoltaic technology has made it possible to harness sunlight directly and convert it into electricity, making solar power a viable and cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels. Similarly, wind energy, harnessed through turbines, has also gained significant traction. The improving efficiency of wind turbines, coupled with the potential to exploit offshore wind resources, has contributed to the surge in wind power generation.
However, the intermittent nature of solar and wind power necessitates the need for efficient storage solutions. Advances in battery technology, grid management, and energy storage systems are thus critical to the further expansion and integration of these renewable sources into the energy mix.
Importance of hydrogen as a renewable energy source
Hydrogen is increasingly being recognized as a critical component of the energy transition. As the most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen has the potential to provide a clean, versatile, and efficient energy solution. It can be produced from a variety of sources, including water, natural gas, and biomass, and can be used in a wide range of applications, from power generation to transportation.
The most significant advantage of hydrogen is that it emits only water when burned, making it an attractive option for reducing carbon emissions. Furthermore, unlike solar and wind power, hydrogen can be stored and transported easily, making it a promising solution for energy storage and grid balancing.
However, the production of hydrogen, especially green hydrogen produced through electrolysis powered by renewables, is currently expensive and energy-intensive. Efforts are underway to improve the efficiency and reduce the costs associated with hydrogen production, which could potentially unlock its full potential as a major player in the energy transition.

Global increase in electric vehicle (EV) adoption
The global increase in electric vehicle (EV) adoption is another key trend shaping the energy transition. As concerns about air pollution and climate change intensify, EVs are emerging as a viable and sustainable alternative to internal combustion engine vehicles.
The shift toward EVs is not just about reducing carbon emissions. It is also about transforming the transportation sector and integrating it with the broader energy system. EVs can act as mobile energy storage units, contributing to grid stability and facilitating the integration of renewables.
The growth of the EV market is driven by advances in battery technology, falling costs, and supportive government policies. However, challenges related to charging infrastructure, range anxiety, and battery disposal and recycling need to be addressed to accelerate EV adoption.
The role of technology in the energy transition
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating the energy transition. From renewable energy technologies to digital platforms for energy management, technology is at the heart of the shift toward a sustainable energy future.
For instance, smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure are enabling better integration of renewables and improving the reliability and efficiency of the energy system. Similarly, energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries and pumped hydro storage, are helping to overcome the intermittency of solar and wind power.
Furthermore, digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things, are transforming the way energy is produced, consumed, and managed. These technologies are enabling the development of decentralized energy systems, promoting energy efficiency, and facilitating the emergence of new business models in the energy sector.
Policy and regulatory impact on the energy transition
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in driving the energy transition. They set the direction for the energy sector, provide incentives for the adoption of renewable energy, and create a favorable environment for innovation and investment.
Policies such as renewable portfolio standards, feed-in tariffs, and carbon pricing are instrumental in promoting the deployment of renewable energy. Similarly, regulations related to vehicle emissions standards, fuel economy standards, and EV incentives are critical in driving the shift toward sustainable transportation.
However, policy and regulatory frameworks need to be robust, stable, and aligned with the long-term goals of the energy transition. Policy uncertainty and regulatory inconsistencies can hinder investment and slow down the pace of the energy transition.
Challenges in implementing energy transition
Despite the significant progress made in the energy transition, several challenges remain. These include technical challenges related to grid integration of renewables, energy storage, and EV charging infrastructure, as well as economic challenges related to the cost competitiveness of renewable energy and economic feasibility of new technologies.
There are also social and political challenges related to public acceptance of renewable energy projects, job displacement in traditional energy sectors, and equity issues in the distribution of energy transition benefits and costs. Furthermore, the energy transition requires substantial investment in infrastructure, technology, and human capital, which can be a significant barrier for developing countries.
These challenges underscore the need for a comprehensive and integrated approach to the energy transition, which involves not only technological innovation but also policy support, market reform, and social engagement.
[Energy transition: How finance professionals can overcome challenges]
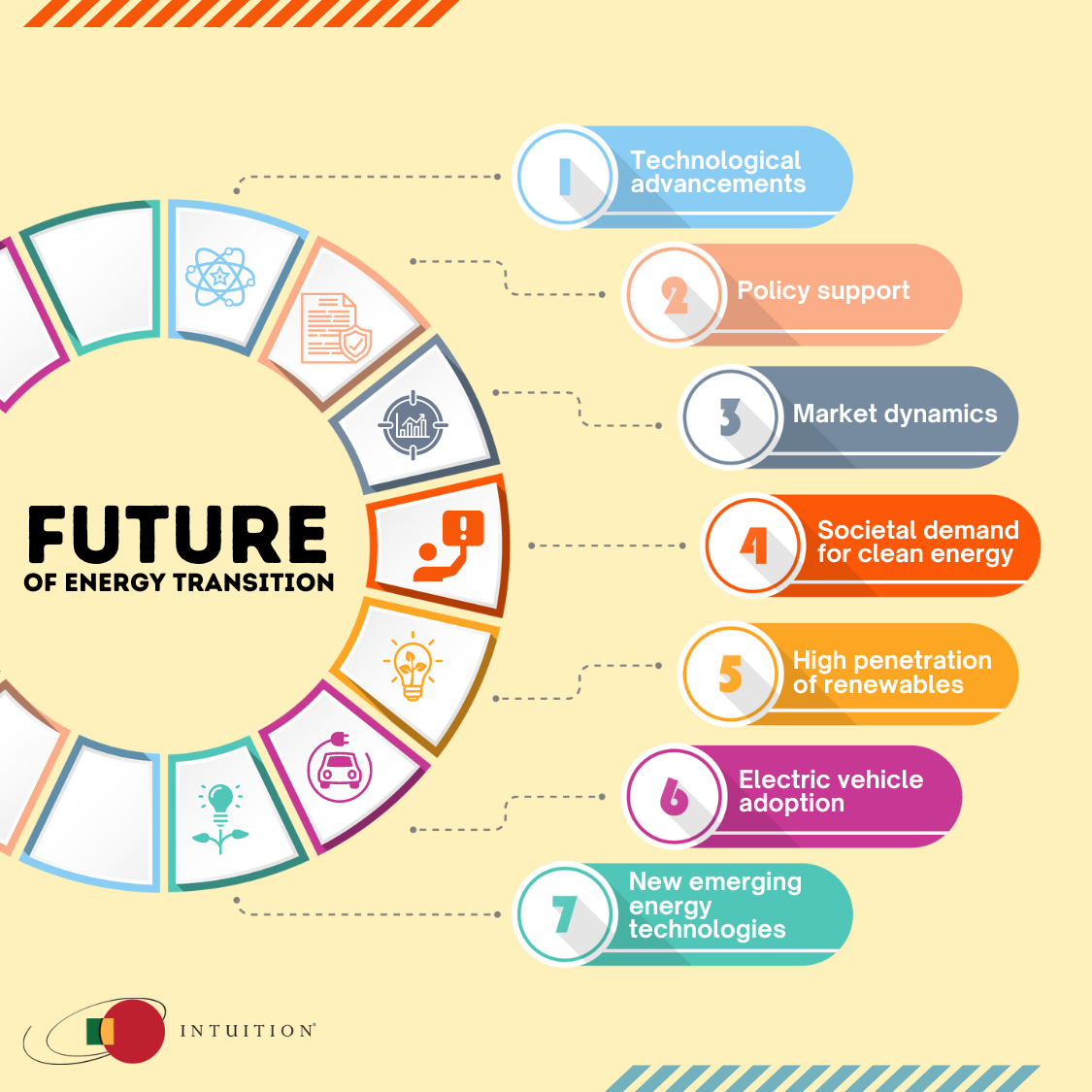
The future of the energy transition: Predictions and insights
Looking ahead, the energy transition is expected to accelerate, driven by technological advancements, policy support, market dynamics, and societal demand for clean energy. The future energy landscape will likely be characterized by a high penetration of renewables, widespread adoption of EVs, and the emergence of new energy technologies and business models.
However, the pace and trajectory of the energy transition will be influenced by several factors, including the evolution of energy policies, the competitiveness of renewable energy, the development of energy storage and hydrogen technologies, and the public’s attitude toward clean energy and sustainable transportation.
The energy transition presents enormous opportunities for businesses, investors, and consumers. Those who can adapt to the changing energy landscape, leverage new technologies, and seize emerging opportunities will be well positioned to thrive in the new energy era.
Successful energy transition initiatives
Several countries and companies have made significant strides in the energy transition, offering valuable insights and lessons for others. For instance, Germany’s Energiewende (energy turnaround) initiative is a leading example of a comprehensive and ambitious energy transition strategy. Through a combination of policy support, market incentives, and public engagement, Germany has dramatically increased its renewable energy capacity and decreased its reliance on fossil fuels.
Similarly, Denmark has become a global leader in wind energy, thanks to its favorable wind conditions, innovative wind turbine technology, and supportive government policies. The country aims to be carbon neutral by 2050, with wind power playing a central role in its energy mix. It currently produces 16.08 terawatt-hours TWh from wind energy, which accounts for 43.8% of the country’s energy consumption.
On the corporate front, companies like Tesla and NextEra Energy are leading the way in EV and renewable energy innovation, respectively. Tesla’s success in the EV market has not only revolutionized the automobile industry but also sparked a global shift toward electric mobility. NextEra Energy, on the other hand, has become the world’s largest producer of wind and solar energy, demonstrating the economic viability and growth potential of renewable energy.
Conclusion
The energy transition is a complex and multifaceted process that requires a concerted and collaborative effort from all stakeholders. While significant challenges remain, the progress made so far provides a strong foundation for a sustainable energy future. The rapid growth of solar and wind energy, the increasing importance of hydrogen as a renewable energy source, and the global increase in electric vehicle adoption are all positive signs of a changing energy landscape.
As we navigate this transformative journey, it is important to continue exploring new technologies, refining policy frameworks, and fostering public engagement. The energy transition is not just about power generation and consumption; it is about creating a sustainable, resilient, and equitable energy system that can meet the needs of a rapidly changing world.


